-

+86-577-57156888
-

-

+86-577-57155869
-
11th Floor, Building 6, Headquarters Economic Park, Yueqing, Zhejiang, China
The Role of Soft Starters in Modern Industrial Applications: Improving Efficiency and Reliability
Industry News-In the fast-paced world of modern industry, ensuring the longevity and efficiency of machinery is critical to maintaining smooth operations. One of the key components helping to achieve this is the soft starter, a device used to control the starting and stopping of electric motors. While it may seem like a simple technology, the benefits of soft starters extend far beyond just controlling the initial surge of current when a motor is activated. With applications across diverse industries such as manufacturing, HVAC, and water treatment, soft starters are becoming indispensable in driving operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
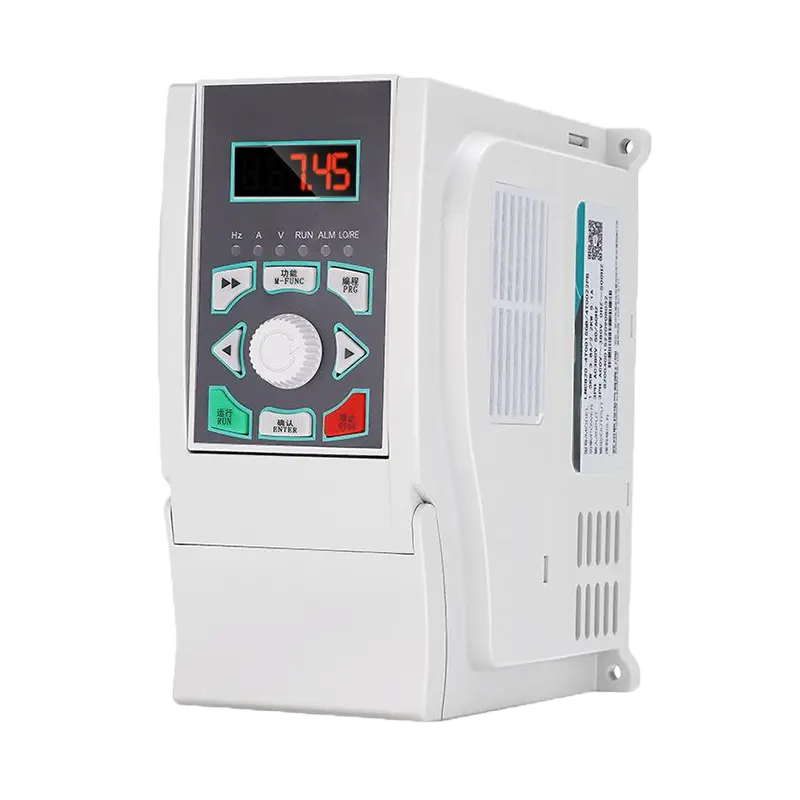
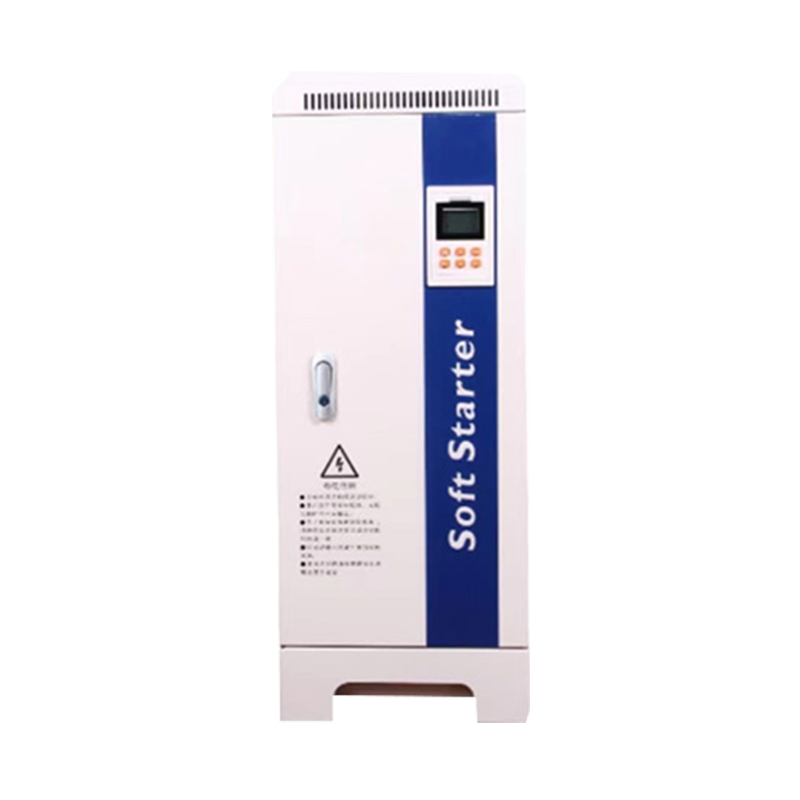
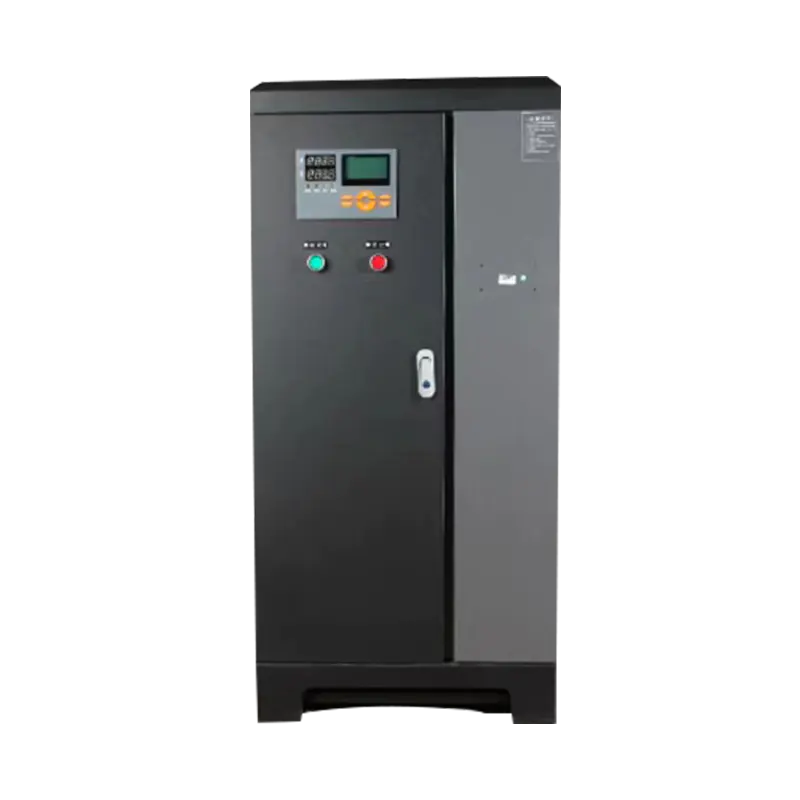
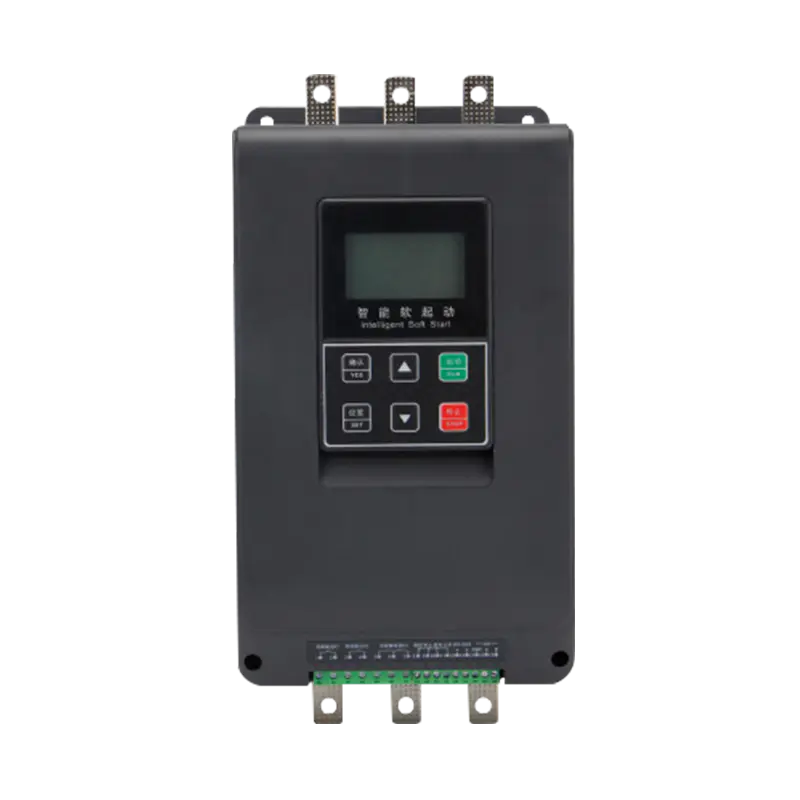
What is a Soft Starter?
A soft starter is an electronic device used to manage the acceleration and deceleration of electric motors, commonly in larger systems like pumps, fans, and conveyors. It functions by gradually increasing the voltage supplied to the motor during startup, thereby limiting the initial surge of electrical current, known as inrush current. This gradual ramp-up reduces the stress on both the motor and the electrical system, minimizing the mechanical wear on components and preventing potential damage from sudden power surges.
Additionally, soft starters can be configured to manage deceleration, ensuring that the motor slows down in a controlled manner rather than stopping abruptly. This smooth deceleration helps prevent issues such as water hammer in pumping systems or excessive vibration in machinery, to improved operational efficiency and safety.
How Soft Starters Work
The core principle behind a soft starter is the control of voltage supplied to the motor. When a motor is powered up, the initial inrush current can be several times higher than the normal operating current, which can cause damage to the motor and the electrical system. Soft starters address this issue by gradually increasing the voltage over a specified time period, allowing the motor to start more smoothly.

Once the motor reaches a preset speed, the soft starter provides full voltage to the motor, allowing it to operate at its performance level. Soft starters also offer the option of controlling the motor’s deceleration, allowing for a gradual reduction in speed when stopping the motor.
Key Benefits of Soft Starters
Reduced Inrush Current: The primary benefit of using a soft starter is the reduction of inrush current during motor startup. By limiting the initial surge of current, soft starters prevent the electrical system from experiencing voltage dips and spikes that could potentially cause damage to the motor or the power distribution network. This feature is particularly important in industrial applications where multiple motors are in use, and large power surges could affect the overall stability of the electrical grid.
Extended Motor Life: The gradual start and stop facilitated by soft starters significantly reduce the mechanical stress placed on motor components. Motors subjected to sudden starts and stops are more likely to suffer from wear and tear, to shorter lifespans and higher maintenance costs. Soft starters ensure that motors experience less stress during the startup and shutdown phases, which helps extend their operational life and reduce the frequency of repairs.
Energy Savings: By controlling the motor’s acceleration and deceleration, soft starters can help optimize the motor's performance, to energy savings. In traditional systems without soft starters, motors may start at full voltage, causing inefficiencies and wasted energy. With a soft starter, energy consumption is optimized, especially in applications where motors are frequently started and stopped.
Smooth Operation: Soft starters contribute to the overall smooth operation of industrial systems by reducing mechanical stresses like vibration, shock loading, and torque fluctuations. This is particularly important in processes like conveyor systems, pumps, and HVAC applications, where abrupt starts and stops can lead to misalignment, damaged parts, or product quality issues. The controlled starting and stopping of motors provided by soft starters contribute to more consistent and reliable operations.
Cost-Effective Solution: Installing a soft starter is often a more cost-effective solution compared to other motor control devices, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs). While VFDs offer more advanced control features, soft starters are more affordable and can still provide significant improvements in terms of motor protection and energy savings. For many applications, especially where speed control is not critical, soft starters present an ideal balance between cost and functionality.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى







 浙公网安备33038202003754号
浙公网安备33038202003754号